In order to use the security interface this features needs to be activated in the file
server-config/application/active-features.xml first.
The settings are configured in the file server-config/application/security.xml afterwards.
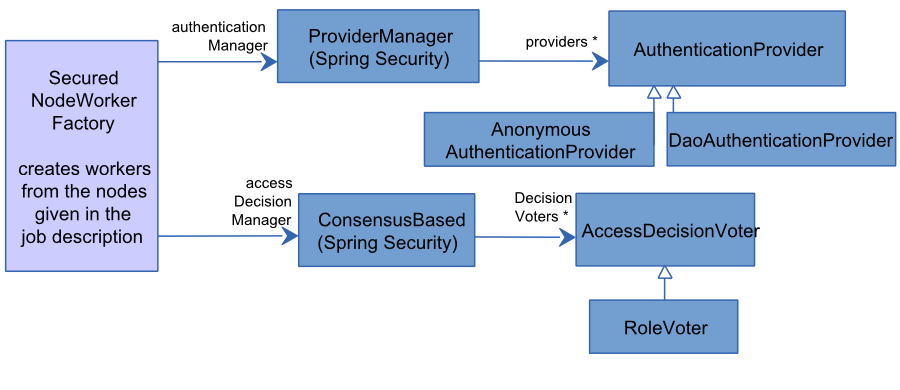
The framework Spring Security is used for authenticating and granting roles. Figure 8.1, “Cooperation between jadice server and Spring Security” shows the cooperation between jadice server and Spring Security:
In order to verify authentication, jadice server refers to the ProviderManager[1]
when generating NodeWorkers. The ProviderManager queries the specified
AuthenticationProviders[2]
whether they accept the credentials of the client. In the example configuration DaoAuthenticationProvider,
which contains hard-coded accounts in the XML configuration, fulfils this function. Moreover, a pre-configured
AnonymousAuthenticationProvider grants clients who access jadice server without credentials the role
ROLE_ANONYMOUS.
Further AuthenticationProvider, for example for the authentication with an
LDAP data base, can be configured here. You will find a more detailed description in Spring Security's documentation.
Furthermore, you will be able to find jar files which are potentially necessary
available for download there. These files can be copied into the directory /server-lib/.
When an authentication has been successfully conducted, the next step (if Nodes which are restricted are to be called) consists in
querying the AccessDecisionManager[3]
whether the authentication meets the restriction. This query is carried out with the help of RoleVoter,
which checks this against the granted roles.
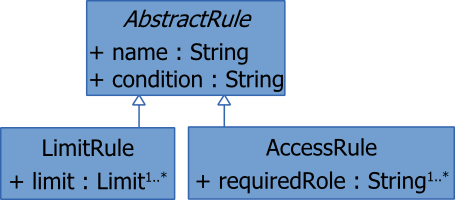
The access to jadice server can be limited in two ways: Either based on AccessRules,
which limit the access to nodes, or based on LimitRules,
which force Limits on Jobs or Nodes:
Figure 8.2. Class Hierarchy of the Security Rules (XML namespace http://www.levigo.com/jadice-server/schema/security)
Rules apply when they comply with the condition framed in the
Spring Expression Language (SpEL).
Beside the logical operators and, or, ! (not) and
the relational operators >, <,
<=, >=, == and
!= pre-defined by SpEL, there are several specific operators
for the evaluation of Nodes and the properties thereof:
Table 8.1. Operators for the Evaluation of Nodes and the Properties Set There
|
Operator |
Description |
|---|---|
|
access('node class name') |
Evaluates as |
|
call('node class name') |
|
|
property('node class name', 'property name') |
Evaluates as the value which a node of a given type has as set property. This can also be applied to properties of properties (see example below). |
|
value('node class name', 'property name') |
There are several possibilities for combining operators:
-
Rules that use access or call can match various node types, for example
access('com.levigo.jadice.server.nodes.StreamInputNode') or access('com.levigo.jadice.server.nodes.StreamOutputNode')A rule with this condition works for all nodes of the types
StreamInputNodeorStreamOutputNode. -
Rules which use property or value can only match one type of node, for example
value('com.levigo.jadice.server.nodes.URLInputNode', 'URLs[0].host') !='localhost' or value('com.levigo.jadice.server.nodes.URLInputNode', 'URLs[0].protocol') != 'http'A rule with this condition works only for
URLInputNodes whose first given URL does not start withhttp://localhost.
The operators isAnonymous() and hasRole('role name') are used for rules which apply depending on the granted roles. These can also be mixed with other operators, for example
access('com.levigo.jadice.server.nodes.URLOutputNode') and !hasRole('ROLE_SUPER')A rule with this conditions applies if a client who is not granted the role ROLE_SUPER tries to
access the URLOutputNode.
Both AccessRules and LimitRules can be phrased
with the help of these conditions. They also have to follow the XML schema definition in the
configuration file. This definition can be found in the jar
file /server-lib/server-core-5.x.y.z.jar under
com/levigo/jadice/server/core/security/jadice-server-security-5.0.xsd.
AccessRules contain one or more elements called requiredRole.
These define which role is necessary if the set condition applies and can be added under the entry
<property name="nodeAccessRules"> in the XML configuration.
LimitRules contain one or more references to Limits, which are set
if the given condition applies. In the XML file these Limits are declared as regular Spring Beans
which need to feature a class and an ID derived from the Limit. When Limits of the same class
are set to Limit.WhenExceedAction ABORT both on the client and in the security
interface, the more restrictive Limit takes precedence.
Rules whose Limits should only be applied to specific nodes can be inserted in the section
<property name="nodeLimitRules">. Rules whose Limits
should be applied to the whole Job can be inserted in the section
<property name="jobLimitRules">. However, please note that
the operators access, call, property and
value cannot be used in the condition.