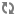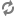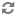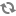Through the support of Java Management Extensions (JMX) jadice server can be monitored and several settings can be changed at runtime. Core components are realized as Managed Beans (MBeans), which enables their close observation.
In order to activate the JMX interface, the following entries have to be
added to the file wrapper/wrapper.conf:
# Activation of the JMX interface wrapper.java.additional.1=-Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.port=61619 wrapper.java.additional.2=-Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.authenticate=false wrapper.java.additional.3=-Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.ssl=false # The numbering has to be consecutive and must not overlap with pre-existing entries.
Please note that no authentication is prescribed in this example. Thus, unauthorized users can also access jadice server via this interface and may disturb its running. However, authentication can be activated. You will find a description of how to activate it in the Java SE Monitoring and Management Guide.
Please connect to jadice server via the tools JConsole or Java VisualVM, which are both
enclosed in Sun's Java Runtime Environment. The following components are essential
in the branch com.levigo.jadice.server (see Figure 9.1, “View of jadice server's MBeans in the Java VisualVM”):
JobScheduler-
This component shows statistics on completed or currently running jobs.
- Pools for MS Office and Libre Office
-
These pools not only show the currently active Office instances but can also be emptied and thus the instanced can be terminated. If job which need Office instances are then begun, new instances are started and the pools are filled anew. Furthermore, you can change the maximum number of started instances here.
Note
This setting does not persist. When jadice server is rebooted the value from the configuration file is loaded.
DefaultServerJob-
This component shows each running job. Jobs can be aborted with
abort. Moreover, statistics on usedNodes, respective threads and the elapsed time of the running jobs can be compiled.